















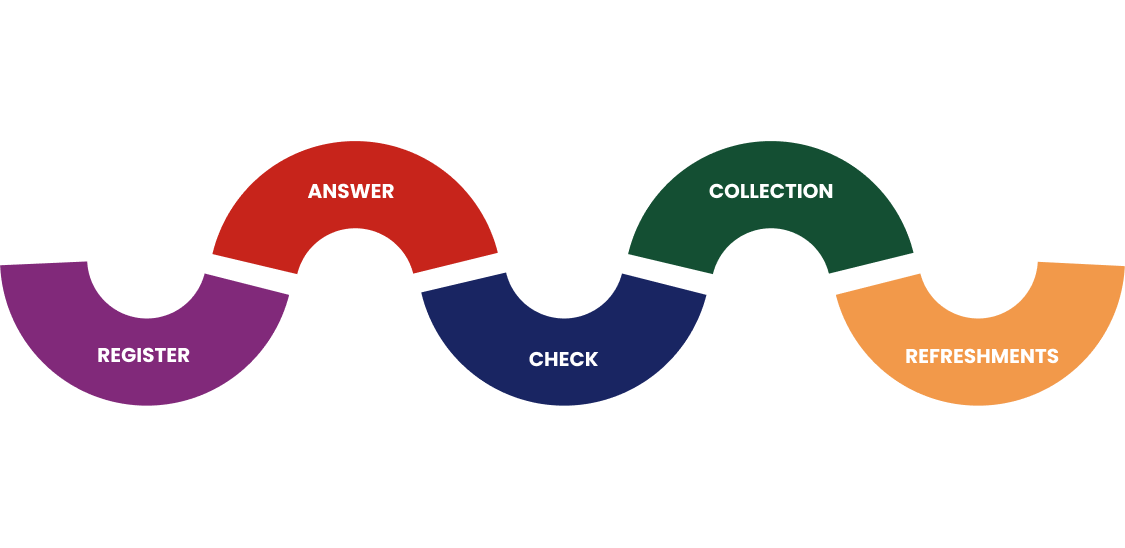
Register online, over the phone, or at our reception. Bring valid ID like a driver’s license or MKBC Donor ID upon arrival.

Register

Register online, over the phone, or at our reception. Bring valid ID like a driver’s license or MKBC Donor ID upon arrival.
Register
Register online, over the phone, or at our reception. Bring valid ID like a driver’s license or MKBC Donor ID upon arrival.

Register

Register online, over the phone, or at our reception. Bring valid ID like a driver’s license or MKBC Donor ID upon arrival.
Register
Register online, over the phone, or at our reception. Bring valid ID like a driver’s license or MKBC Donor ID upon arrival.

Register
Blood Basics
- What are the four main blood types?
The four main blood types are: A, B, AB and O
- What is the rarest blood type?
The rarest blood type is the one not on the shelf at the moment a patient needs it.
- What is a Universal Blood Donor?
A Universal Blood Donor belongs to the O- blood group. The red blood cells of a universal blood donor may be transfused to anyone regardless of their blood type.
- What is a Universal Plasma Donor?
A Universal Plasma Donor belongs to the AB blood group (positive or negative). The plasma of those belonging to the AB blood group may be transfused to anyone regardless of blood type.
- How many people are O+?
1 person in 3 in the United States is O+. That’s 37.4% of the population.
- How many people are O-?
1 person in 15 in the United States is O-. That’s 6.6% of the population.
- How many people are A+?
1 person in 3 in the United States is A+. That’s 35.7% of the population.
- How many people are A-?
1 person in 16 in the United States is A-. That’s 6.3% of the population
- How many people are B+?
1 person in 12 in the United States is B+. That’s 8.5% of the population.
- How many people are B-?
1 person in 67 in the United States is B-. That’s 1.5% of the population
- How many people are AB+?
1 person in 29 in the United States is AB+. That’s 3.4% of the population.
- How many people are AB-?
1 person in 167 in the United States is AB-. That’s 0.6% of the population.
- How long does blood last?
Red Blood Cells can be stored for up to 42 days, while platelets can only be stored for up to 7 days – two of which are used for testing
- What are Red Blood Cells?
Red Blood Cells are biconcave disks that contain hemoglobin and carry oxygen to the body’s organs and tissues. Mature Red Blood Cells have no nucleus.
- What are Platelets?
Platelets are small fragments of blood cells that initiate blood clotting and control bleeding.
- What is Plasma?
Plasma is a pale yellow mixture of water, salts and proteins, including soluble clotting factors; Plasma is 90 percent water and constitutes 55 percent of blood volume.
- What is Cryoprecipitate?
Cryoprecipitate is a frozen blood product prepared from plasma that contains clotting factors. It is used primarily to prevent or control massive bleeding in situations such as traumatic injury or major cardiac surgery.
- How does blood keep me healthy?
Blood fights against infection and helps heal wounds.
- Who needs platelet transfusions most?
Cancer patients are the #1 group requiring Platelet transfusions for life-saving treatments.
- What are some examples of blood use?
Premature infants may use at least 1 – 4 units of Red Cells.
Accident victims may use at least 5 – 100 units of Red Cells.Burn victims may use at least 20 units of Platelets.
Cancer patients may use at least 3 – 10 units of Red Cells and 10 – 30 units of Platelets.
Sickle Cell patients may use at least 10 – 20 units of Red Cells.
Heart surgery patients may use at least 3 – 8 units of Red Cells, 1 – 10 units of Platelets and 2 – 5 units of Plasma.
Organ transplant patients may use at least 10 – 30 units of Red Cells, 10 – 30 units of Platelets, 10 – 20 units of Plasma and 20 bags of Cryoprecipitate.
Bone marrow transplant patients may use at least 15 – 20 units of Red Cells and 100 – 120 units of Platelets. - What is a unit?
A unit of blood is approximately 525 mL, which is roughly the equivalent of one pint.
A unit of blood is approximately 525 mL, which is roughly the equivalent of one pint.
- Do blood types differ between ethnic groups?
Yes. About 57% of the Latino population is type O, the blood type in greatest demand. That share is 51% for African Americans, and only about 45% for white Caucasians. As certain population groups continue to increase, so does the need for type O blood. It is critical that more Latino and African American donors give blood regularly to ensure that patient needs can be met.
- Are blood substitutes available?
No, there are currently no substitutes for human blood. The only source is you, the volunteer blood donor.
- Why do anemic patients need blood transfusions?
Anemic patients require blood transfusions in order to improve oxygen transport to organs and tissues.
- How many donors are needed to meet the needs of transfusion patients?
Approximately 350 donors are needed to meet the daily needs of transfusion patients in the 35 hospitals served by Miller-Keystone Blood Center.
- How much blood is used each day in the United States?
Approximately 43,000 units of blood are used each day in the United States.
- How much blood is used in our community?
The following approximate quantities of life-saving blood products are utilized on annual basis in the counties served by Miller-Keystone Blood Center:
Approximately 60,000 units of red blood cells
Approximately 16,000 units of platelets
Approximately 20,000 units of plasma - How many pints of blood are in the human body?
Between 8-12 pints of blood are in the body of an average adult.
A newborn baby has about one cup of blood in his/her body. - How many people will need blood in their lifetime?
Statistics show that 25% or more of us will require blood at least once in our lifetime.
- Is there an age limit for blood donation?
Individuals must be 16 years of age or older to donate blood. State law requires written consent by a parent or guardian for 16-year-olds to donate blood. Please print both the front and back of the form linked below and present both pages at the time of your donation.
16-year-old Consent Form (8/21)Persons 17 years of age or older may donate without consent of a parent or guardian (unless consent is required by their high school).
There is no upper age limit for blood donation.
- Can someone with Hemochromatosis donate blood?
Hemochromatosis is a disorder that interferes with iron metabolism, and results in excess iron deposits throughout the body. The goal of treatment is to remove excess iron from the body through the removal of blood from the body (referred to as therapeutic phlebotomy). The amount of blood, and the frequency with which the blood is removed from the body, is determined by the patient’s physician on a case-by-case basis.
In 2006 with a physician’s prescription, MKBC obtained an FDA variance to draw blood from patients with hemochromatosis and distribute for transfusion. These individuals are able to undergo their blood removal treatments, while also contributing to our community’s blood supply, as it is very safe to transfuse these blood products to hospital patients. These donors must qualify in every other was as volunteer community blood donors.
For more information on this process, call MKBC at 800-B-A-DONOR (223-6667) ext. 1279 and ask to speak with someone in our Special Collections department. - Can I get paid to donate blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- Is MKBC testing for COVID-19 antibodies?
MKBC does not test for COVID-19 antibodies.
- Can I donate if I have received a COVID19 / coronavirus vaccine?
Individuals receiving the COVID-19 vaccine or the Monoclonal Antibody Infusion are accepted for whole blood, red cell, platelet or plasma donation. (please be prepared to confirm which vaccine you received – manufacturer and date)
- I have never donated blood before. What can I expect when I donate?
Thank you for making the decision to donate blood!
While appointments are preferred, walk-in donors are welcome and accepted as time permits. Schedule online at GIVEaPINT.org or over the phone at 800-B-A-DONOR.
Before you arrive for your appointment, please be sure to keep hydrated and eat a hearty meal.
When you arrive, please be prepared to provide us with valid identification, such as a driver’s license or your MKBC Donor ID. AIf you answered your medical history questions at home using iScreen®, present the barcode. If you did not answer your medical history questions using iScreen®, then you will answer them at the blood drive/donation center.
A trained medical screener will do a health check taking your blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and testing your iron level. If your medical history questionnaire and your health check is successful, our staff will guide you to the most needed donation type. If whole blood is collected, the donation will take approximately 6-10 minutes. Automated collection of platelets, plasma, and red blood cells may take 30 minutes to 2 hours.
When you have completed your lifesaving blood donation, you will be directed to the canteen area where you can relax and be served refreshments. Whole blood donors must remain in the canteen for 15 minutes. And that is it! You will have shared your desire to save the life of others. While you may never know the recipient of your blood donation, you can be assured that they and their family are truly grateful.
Blood Safety
- Is it safe to give blood?
Giving blood is generally considered safe. However, any procedure involves some degree of risk. Sterile procedures and disposable equipment are used in all Miller-Keystone Donor Centers and Blood Drives. Each needle is used once and then safely discarded and disposed.
- Can I get HIV from donating blood?
No – you cannot contract HIV or other viral diseases by giving blood. Sterile procedures and disposable equipment are used in all Miller-Keystone Donor Centers and Blood Drives. Each needle is used once and then safely discarded and disposed.
- What tests are administered to ensure that my blood is safe for transfusion to patients?
Every blood donation is screened for the following:
ABO and Rh blood types.
Unexpected red cell antibodies that result from prior transfusions, pregnancy, etc.
Antibody to Treponema pallidum (syphilis).
Antibody to HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).
Antibody to HCV (hepatitis C virus).
Antibody to HBC (hepatitis B core antigen).
HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen).
Antibody to HTLV (Human T- Lymphotropic virus)
Antibody to Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas’ Disease)
Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) for HCV, HBV, HIV, West Nile Virus (WNV) and Babesia - Can I get a free AIDS test when I donate blood?
You should not give blood to get tested for AIDS. Using blood donation as a way to get tested will put the blood supply at risk and endanger the lives of patients in our local hospitals. If you are at risk of getting AIDS or other infectious diseases, do not give blood. Individuals at risk for contracting HIV should contact their local health department for free and confidential AIDS testing.
- If my blood tests positive for disease, will I be informed?
Yes. Donors who are confirmed positive for any abnormalities or infectious disease are notified immediately and offered counseling by Miller-Keystone Blood Center’s Medical Department.
- How will Miller-Keystone Blood Center contact me if I have a disease?
Miller-Keystone Blood Center practices strict privacy and confidentiality standards. We will contact you by certified letter containing instructions on how to manage positive test results. Should you have any questions regarding the letter, please contact the MKBC Medical Department. We will not disclose information regarding positive blood test results to anyone but the donor without their consent, except as required by law.
- What happens if I donate blood and realize afterward that I shouldn’t have because I may have been exposed to HIV or another disease?
PLEASE CONTACT OUR MEDICAL DEPARTMENT AT 1-800-223-6667 x1247 or x1297
- If you remember important health information that you may have NOT give us.
- If you become ill.
- If you decide that your blood MAY NOT BE SAFE to give to another person.
- If you feel you need immediate medical attention, please do not hesitate to contact your family physician or the nearest emergency room. if this does occur kindly inform our Medical Department as soon as possible.
- What is Chagas disease?
About 100,000 people in the United States are thought to be infected with Trypanosoma cruzi, the parasite that causes Chagas’ disease, a potentially life-threatening illness that primarily impacts the cardiac and digestive system. Up to 20 million people are believed to be infected in Mexico, Central and South America. Miller-Keystone Blood Center tests each first time blood donor for Chagas’ disease and discards any positive units.
- What is TRALI?
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a serious blood transfusion complication thought to be most commonly caused by white blood cell antibodies present in the plasma component of blood products. When transfused, these antibodies sometimes activate a type of white blood cell that causes plasma to leak into the lungs, resulting in fluid accumulation – a condition referred to as acute pulmonary edema.
- What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle Cell Disease is a result of a mutation to the gene responsible for hemoglobin. This mutation causes a person’s Red Blood Cells to change from disk shaped to crescent shaped. The deformed cells may clog the body’s small blood vessels, causing extreme pain. In addition, these abnormally shaped cells die early causing a constant shortage of red blood cells, causing patients to become chronically anemic and increasing their chance of infections and stroke, as well as tissue and organ damage.
One in 500 African-Americans suffer from sickle cell anemia, while one in 12 African-Americans carry the sickle cell trait. Patients with the disease may need 15 to 25 blood transfusions each year. - Does Miller-Keystone Blood Center pay donors for blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors from the community. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- How much of the United States population is eligible to donate blood?
40% of the US population is eligible for blood donation, yet less than 5% actually donate blood on an annual basis.
- What blood types does Miller-Keystone Blood Center often run short of?
MKBC is chronically short of Group O Positive and Group O negative Red Blood Cells. In addition, there is a chronic shortage of Group AB Plasma. However, all blood groups are needed throughout the year.
- When does Miller-Keystone Blood Center experience blood shortages?
Cyclic shortages typically occur during summer months and winter holidays due to school closings, vacations, seasonal illness, holidays, and inclement weather. However, blood shortages may occur at any time when there is an increased demand or decreased donor participation.
- Is MKBC testing for COVID-19 antibodies?
MKBC does not test for COVID-19 antibodies.
- Can I donate if I have received a COVID19 / coronavirus vaccine?
Individuals receiving the COVID-19 vaccine or the Monoclonal Antibody Infusion are accepted for whole blood, red cell, platelet or plasma donation. (please be prepared to confirm which vaccine you received – manufacturer and date)
Donating Blood
- How often can I donate?
Give Whole Blood every 56 days, up to six times per year.
Give Platelets every two weeks, up to 24 times per year.
Give Plasma every four weeks.
Give Automated Red Cells every 112 days. - Will it hurt when you insert the needle?
Lightly pinch the fleshy, soft underside of your arm. Did that hurt? That pinch is similar to what you will feel when the needle is inserted.
- How long does a blood donation take?
From registration to release, the entire donation process takes about 45 minutes to two hours, depending on the type of donation. The actual collection of blood products will take 10 to 90 minutes.
Whole Blood = 45 minutes to 1 hour
Automated Red Cells = 1 to 1.5 hours
Red Cell + Platelet = 1.5 to 2 hours
Red Cell + Double Platelet = 1.5 to 2 hours
Single Platelet = 1 hour 20 minutes
Double Platelet = 1.5 to 2 hours
Plasma + Platelet = 1.5 hours
Jumbo Plasma = 20 minutes
Times do vary by person depending on factors like the donor’s health history. - How long does it take to donate whole blood?
The actual donation of a pint of Whole Blood unit takes eight to 10 minutes.
- How long does it take to donate platelets?
The actual donation of Platelets takes 60 to 90 minutes.
- How long does it take to donate plasma?
The actual donation of Plasma takes about 90 minutes.
- How much blood am I donating?
Imagine a two liter container of soda. When you give blood, you’re donating approximately ¼ of a two liter container, or 525 mL.
- How long will it take to replenish the pint of blood I donate?
It will take your body up to eight weeks for complete replacement of Red Blood Cells. Plasma is replaced within 48 hours.
- Why does Miller-Keystone Blood Center ask so many personal questions when I give blood?
Miller-Keystone’s #1 priority is safety – of the blood supply and our blood donors! These requirements are in place and regulated by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure that your blood is safe for patients and that it is safe for you to donate.
- What does Miller-Keystone Blood Center do with my blood?
After your donation, Miller-Keystone Blood Center performs rigorous testing on your blood to ensure its safety for patients in our local hospitals. After testing, your blood is properly labeled, stored and eventually shipped to one of the many hospitals served by Miller-Keystone Blood Center. Sometimes plasma is sent for further manufacturing into lifesaving medicines.
- Does Miller-Keystone Blood Center pay donors for blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors from the community. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- Can someone with Hemochromatosis donate blood?
Hemochromatosis is a disorder that interferes with iron metabolism, and results in excess iron deposits throughout the body. The goal of treatment is to remove excess iron from the body through the removal of blood from the body (referred to as therapeutic phlebotomy). The amount of blood, and the frequency with which the blood is removed from the body, is determined by the patient’s physician on a case-by-case basis.
In 2006 with a physician’s prescription, MKBC obtained an FDA variance to draw blood from patients with hemochromatosis and distribute for transfusion. These individuals are able to undergo their blood removal treatments, while also contributing to our community’s blood supply, as it is very safe to transfuse these blood products to hospital patients. These donors must qualify in every other was as volunteer community blood donors.
For more information on this process, call MKBC at 800-B-A-DONOR (223-6667) ext. 1279 and ask to speak with someone in our Special Collections department. - Can I get paid to donate blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- Is MKBC testing for COVID-19 antibodies?
MKBC does not test for COVID-19 antibodies.
- Can I donate blood if I recently received a flu shot?
Yes! Assuming you meet all other general eligibility requirements, individuals receiving a flu shot are accepted for blood donation if they are not currently experiencing any signs or symptoms of the flu.
- Can I donate if I have received a COVID19 / coronavirus vaccine?
Individuals receiving the COVID-19 vaccine or the Monoclonal Antibody Infusion are accepted for whole blood, red cell, platelet or plasma donation. (please be prepared to confirm which vaccine you received – manufacturer and date)
- I have never donated blood before. What can I expect when I donate?
Thank you for making the decision to donate blood!
While appointments are preferred, walk-in donors are welcome and accepted as time permits. Schedule online at GIVEaPINT.org or over the phone at 800-B-A-DONOR.
Before you arrive for your appointment, please be sure to keep hydrated and eat a hearty meal.
When you arrive, please be prepared to provide us with valid identification, such as a driver’s license or your MKBC Donor ID. AIf you answered your medical history questions at home using iScreen®, present the barcode. If you did not answer your medical history questions using iScreen®, then you will answer them at the blood drive/donation center.
A trained medical screener will do a health check taking your blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and testing your iron level. If your medical history questionnaire and your health check is successful, our staff will guide you to the most needed donation type. If whole blood is collected, the donation will take approximately 6-10 minutes. Automated collection of platelets, plasma, and red blood cells may take 30 minutes to 2 hours.
When you have completed your lifesaving blood donation, you will be directed to the canteen area where you can relax and be served refreshments. Whole blood donors must remain in the canteen for 15 minutes. And that is it! You will have shared your desire to save the life of others. While you may never know the recipient of your blood donation, you can be assured that they and their family are truly grateful. - What is the Thank the Donor Program?
“Thank the Donor ®” (TtD) allows blood donors and transfusion recipients to anonymously connect, enabling the recipient to thank the donor for their lifesaving generosity via email. It is currently used in many of the hospitals we serve.
- Can I Bring My Child To The Blood Center?
Blood donations are urgently needed at this time, and we are grateful for your lifesaving gift. Please note:
- MKBC cannot accommodate children in any biohazard area including, but not limited to, medical interview, collection area or within the canteen
- Children under the age of 16 are not permitted in any area of the donation site except for the designated waiting area
- Children under the age of 12 must have an adult sit and wait with them in the designated waiting area; children over the age of 12 may wait alone in the waiting area
- MKBC staff members may not be the accompanying adult with children under the age of 12 in the waiting area during the staff member's typical working hours
- Children are not permitted on the mobile coach vehicles under any circumstances
If your child(ren) must accompany you to our donor center, we ask you that you bring along a family member or friend to watch over them during your donation. If this is not possible, please contact us to reschedule your appointment. Thank you!
- Do I need an appointment?
While appointments are preferred, walk-in donors are welcome and accepted as time permits.
Eligibility
- How often can I donate blood?
Give Whole Blood every 56 days, up to six times per year.
Give Platelets every two weeks, up to 24 times per year.
Give Plasma every four weeks.
Give Automated red cells every 112 days. - Who can donate blood?
If you’re in good health, 16 years of age or older, and weigh a minimum of 110 pounds, you are most likely eligible for blood donation. There is no upper age limit for blood donors. Click here for general eligibility requirements. If you have more specific questions regarding your eligibility, please contact Miller-Keystone Blood Center’s Donor Resources Department at 1-800-B-A-DONOR.
- How do I maintain iron balance?
While eating a well-balanced diet is important for all donors, simply eating iron-rich foods may not replace all the iron lost from blood donation. Taking multivitamins with iron or iron supplements, either prescribed or over the counter (from a drug store) may help replace iron lost. Iron supplements vary in name and proportion of iron within the tablet/caplet. The most effective dose, type of iron supplement, and length of treatment are currently being studied. Current recommendations range from one typical multivitamin with iron (19 mg iron) to elemental iron caplets (45 mg iron) for up to three months. Your physician or pharmacist may be able to assist you in deciding what dose, type and duration of iron supplement to choose.
- Can I donate if I am anemic?
Potential donors can only be accepted for blood donation if they have a hemoglobin or hematocrit that meets a Federally established level; we are unable to accept donors who have a hemoglobin or hematocrit below this Federally established cutoff. Before each donation, your Hematocrit (iron) level will be checked. As longs as levels are within acceptable range on the day of donation, you are most likely eligible to donate blood; however, individual assessment by a screener may be required.
We are not able to draw a unit of blood from someone who is truly anemic. Regular blood donation can deplete iron stores unless an iron rich diet is consumed on a regular basis. In some cases supplemental iron may be taken. If a donor is being treated for anemia, a discussion should take place between the donor and his her physician to determine if blood donation is in his/her best interest. - Can I donate if I have had cancer?
Individuals with Skin Cancers (such as Squamous or Basal Cell Carcinoma) may donate blood, and those with Melanoma may be eligible after evaluation by our Medical Director.
Persons with other forms of cancer may donate blood after being in remission for at least one year.
However, individuals with Blood Cancer (Leukemia or lymphoma) are not eligible to donate blood. - Can I donate blood if I have a tattoo?
If an individual’s tattoo was applied at a medical facility (eg Cosmetic Surgeon), tattoo was medically removed and have no open wounds, or the tattoo was applied at a state regulated entity in the state of New Jersey, they are eligible to donate blood.
However, if a potential donor had a tattoo applied in a state other than the state of New Jersey, they are not eligible for three (3) months from the date the tattoo was applied. - Can someone with diabetes donate blood?
Donors with diabetes prescribed insulin and/or oral medication are eligible to donate, as long as all other medical requirements are met. Please note: if you have used bovine-derived insulin, you are not eligible to donate.
- Can I donate if I’m taking medications?
If prescribed antibiotics, you are eligible to donate 24 hours after your last dose. If taking antibiotics as a preventative measure, you are eligible to donate.
Other medications may require a temporary or permanent deferral. The list of medications that may prevent you from donating is constantly changing, so if you were deferred in the past, we encourage you to confirm your eligibility from time to time, as you may once again become eligible.
For the most up-to-date list of acceptable / non-acceptable medications, click here! Medication Deferral List Definitions - Can I donate if I have traveled outside the country?
Traveling outside of the United States will not automatically defer you from giving blood, however there are temporary restrictions are placed on donors who have visited countries with a high risk of Malaria, and from time to time other infectious diseases. Click here for additional information outlining temporary and/or indefinite deferrals as a result of travel.
- Can I bring my child with me to donate?
It is MKBC policy to not allow children in our Donor Room or Canteen areas for their safety. They cannot be left unattended in our Waiting Room, so we ask that you bring along a family member or friend to watch over them during your donation. If this is not possible, please contact us to reschedule your appointment. Thank you!
- Are service animals permitted while donating?
A trained service animal is permitted within the Waiting, Screening, Phlebotomy and Canteen areas of our fixed sites, mobiles and coaches. Service animals shall be in the control of their handler at all times. Service animals should not be left unattended.
- Does Miller-Keystone Blood Center pay donors for blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors from the community. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- Is there an age limit for blood donation?
Individuals must be 16 years of age or older to donate blood. State law requires written consent by a parent or guardian for 16-year-olds to donate blood. Please print both the front and back of the form linked below and present both pages at the time of your donation.
16-year-old Consent Form (8/21)Persons 17 years of age or older may donate without consent of a parent or guardian (unless consent is required by their high school).
There is no upper age limit for blood donation.
- Can someone with Hemochromatosis donate blood?
Hemochromatosis is a disorder that interferes with iron metabolism, and results in excess iron deposits throughout the body. The goal of treatment is to remove excess iron from the body through the removal of blood from the body (referred to as therapeutic phlebotomy). The amount of blood, and the frequency with which the blood is removed from the body, is determined by the patient’s physician on a case-by-case basis.
In 2006 with a physician’s prescription, MKBC obtained an FDA variance to draw blood from patients with hemochromatosis and distribute for transfusion. These individuals are able to undergo their blood removal treatments, while also contributing to our community’s blood supply, as it is very safe to transfuse these blood products to hospital patients. These donors must qualify in every other was as volunteer community blood donors.
For more information on this process, call MKBC at 800-B-A-DONOR (223-6667) ext. 1279 and ask to speak with someone in our Special Collections department. - Can I get paid to donate blood?
No. Miller-Keystone Blood Center only accepts volunteer blood donors. According to the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates all US blood banks, blood or plasma from people who have been paid to donate cannot be used for transfusion to humans.
- Can I donate blood if I recently received a flu shot?
Yes! Assuming you meet all other general eligibility requirements, individuals receiving a flu shot are accepted for blood donation if they are not currently experiencing any signs or symptoms of the flu.
- Can I donate if I have received a COVID19 / coronavirus vaccine?
Individuals receiving the COVID-19 vaccine or the Monoclonal Antibody Infusion are accepted for whole blood, red cell, platelet or plasma donation. (please be prepared to confirm which vaccine you received – manufacturer and date)
- I have never donated blood before. What can I expect when I donate?
Thank you for making the decision to donate blood!
While appointments are preferred, walk-in donors are welcome and accepted as time permits. Schedule online at GIVEaPINT.org or over the phone at 800-B-A-DONOR.Before you arrive for your appointment, please be sure to keep hydrated and eat a hearty meal.
When you arrive, please be prepared to provide us with valid identification, such as a driver’s license or your MKBC Donor ID. AIf you answered your medical history questions at home using iScreen®, present the barcode. If you did not answer your medical history questions using iScreen®, then you will answer them at the blood drive/donation center.A trained medical screener will do a health check taking your blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and testing your iron level. If your medical history questionnaire and your health check is successful, our staff will guide you to the most needed donation type. If whole blood is collected, the donation will take approximately 6-10 minutes. Automated collection of platelets, plasma, and red blood cells may take 30 minutes to 2 hours.
When you have completed your lifesaving blood donation, you will be directed to the canteen area where you can relax and be served refreshments. Whole blood donors must remain in the canteen for 15 minutes. And that is it! You will have shared your desire to save the life of others. While you may never know the recipient of your blood donation, you can be assured that they and their family are truly grateful.
iScreen
- What is iScreen?
iScreen is Miller-Keystone Blood Center’s secure & private, online Donor History Questionnaire. iScreen can be used to complete your Donor History Questions before arriving at a blood collection center or blood drive (the FDA requires that your online Donor History Questionnaire be completed on the same day as your donation).
- Are the responses kept confidential?
Your name is the only personal information printed on your donor receipt. After you complete your Donor History Questions, a secure bar code is generated. This bar code can only be read by software accessible at Miller-Keystone Blood Center donation locations. iScreen is designed to timeout after a period of inactivity so no one can access your confidential Donor History Question responses.
- How does it work?
Access iScreen from GIVEaPINT.org on the day of your donation. iScreen is a secure internet based system that will allow you to answer your Donor History Questions confidentially. Then you will be able to print out or email to your smart phone a bar-coded receipt that contains your hidden responses which you will bring with you when you donate.
- When can I complete my Donor History Questions using iScreen?
You can complete your Donor History Questions using iScreen the day of your donation. Questions completed prior to midnight the day of your donation will be invalid and you will have to repeat the interview prior to your donation.
- What are the benefits of using iScreen?
Save time – by completing your Donor History Questions prior to arriving for your blood donation, you could reduce the amount of time spent at the blood center or donation location.
Privacy – a Miller-Keystone Blood Center staff member will no longer ask your Donor History Questions, which the FDA requires we ask prior to every donation. Only questions skipped or which need further follow up will be asked.
Convenience – you can complete your Donor History Questions anytime and anywhere, the day of your donation.
Help save the environment – iScreen is a paperless option. - Are the responses kept confidential?
Your name is the only personal information printed on your donor receipt. After you complete your Donor History Questions, a secure bar code is generated. This bar code can only be read by software accessible at Miller-Keystone Blood Center donation locations. iScreen is designed to timeout after a period of inactivity so no one can access your confidential Donor History Question responses.
- What types of software are compatible with iScreen?
iScreen requires Adobe Reader version 9.4 or newer.
Recommended iScreen browsers are: Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari (current versions).
iScreen is not currently supported on Android or Apple iOS tablets/mobile devices. Coming soon!
- What are the technical requirements and limitations?
Miller-Keystone Blood Center cannot provide technical support outside of our own network. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.
iScreen requires Adobe Reader version 9.4 or newer.
Recommended iScreen browsers are: Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari (current versions).
iScreen is not currently supported on Android or Apple iOS tablets/mobile devices. Coming soon!
- I can’t access iScreen from my work computer?
Miller-Keystone Blood Center makes the iScreen available to all internet users. However, some employers may restrict access to certain website. If you have trouble accessing iScreen at your place of business please contact your technical support staff.
- Will I have to answer the questions again when I arrive to donate?
There may be rare cases you may have to answer all or some of the questions again. Those rare cases may be:
Your donor receipt is lost or unreadable by the scanner.
iScreen is not completed on the same day as your blood donation.
If you didn’t answer a specific question, we will need to ask that question again. - What if I answer a question incorrectly?
You can change your answers at any time during the iScreen process by selecting the “Review Answers” button. If you have already completed the iScreenprocess and printed or emailed your iScreen donor receipt, you should notify a Miller-Keystone Blood Center Collection Specialist at the time of your donation.
- What if I’m not sure how to answer a question?
You can skip a question and review it with a Miller-Keystone Blood Center Collection Specialist at the time of your donation.
- What if I lose my donor receipt?
If your donor receipt is lost you will need to complete iScreen again online or at the donation site.
- Why do I have to answer the Donor History Questions every time I donate?
As a safety measure for both the recipient and the donor, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires that we ask the Donor History Questions prior to every donation.
Platelet Donations
- How often can I give Platelets?
You can give Platelets every two weeks, up to 24 times per year.
- What are Platelets and how are they used?
Platelets are tiny, colorless, disc-shaped particles circulating in blood that help control bleeding and bruising. Platelets activate substances in plasma which form clots and promote wound healing. Since platelets help control bleeding, they are very important for heart surgery patients, burn victims, organ transplant patients, bone marrow transplant patients, accident victims, premature babies, and especially cancer patients.
Cancer is the #1 patient group that needs Platelet transfusions. Some cancer treatments cause decreased blood and platelet production in the bone marrow. When Platelet levels fall too low, Platelets are transfused into patients to replenish their supply and prevent life-threatening bleeding. Many cancer patients require daily Platelet transfusions for several weeks.
Platelets have the shortest shelf life of all blood components, lasting only seven (7) days. There is a constant need of Platelets for life-saving treatments. - What is Apheresis?
Apheresis is the process by which platelets and other blood components are collected from the blood using a cell separator. Blood is drawn from the donor and Platelets, Plasma and/or Red Cells are collected by the cell separator. The remaining components are returned to the donor along with saline fluid. Each procedure take about one-and-one-half to two hours. Donor may watch movies, read or simply relax during the donation. The word itself is derived from the Greek word “aphaeresis” meaning “to take away.”

